Redistribution of intensities of DNA infrared bands in the polarized spectra under the weak electromagnetic field
Galina DovbeshkoDepartment of Physics of Biological Systems, Institute of Physics, Nat. Ac.Sci Ukr.,Prospect Nauki,46 ,252650,Kiev,-22,Ukraine,e-mail:galina@dpbs-3.kar.net
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
The changes in parameters of vibrational spectral bands of DNA molecules caused by the weak microwave field have been investigated by IR spectroscopy. Drastic changes have been found in the intensities and fine structure of C=O and PO2 bands in the polarized spectra of the irradiated samples of DNA as compared with the reference samples in the 1700-1000 cm-1 region.
Keywords:
DNA molecule, infrared spectra, polarized spectra, vibrational bands, weak microwave irradiation.INTRODUCTION
The structure of DNA is a subject of great interest due to its important functional-oriented properties and yet not fully predictable behaviour. There is a lot of experimental data, gene library, big scientific programmes on DNA studies in the world. But at present a physical theory of nonlinear conformational DNA dynamics and its structural changes is absent.
The aim of our study is to investigate the structural peculiarities of DNA caused by the weak electromagnetic field as well as some manifestations of the dynamical structure of DNA [1]. Our approach is based on the assumption of the stereochemical nonrigidity of the fragments, which form the DNA molecule [2-4], as it takes place in liquid crystals under external stimuli. For such system as the DNA molecule formed by fragments which slightly differ from each other and can be in states whose energies also only slightly differ from each other, small changes of the total energy can be accompanied by drastic changes of the structure of the molecule as a whole (tertiary structure, the system of H-bonds, etc.). One can suppose that the weak electromagnetic field could lead to some small structural changes in the molecular fragments and, as a result, to some rearrangement of DNA spacial structure as a whole within some segments of the DNA molecule.
2. METHODS AND MATERIALS
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy was used for structural studies[5]. IR spectra were recorded with IFS 48 Bruker and PE 599 spectrometers. Polarized IR spectra were recorded with IKS
40 (LOMO) spectrometer with a polyethylene polarizer put into the sample room of the spectrometer. The polarizer angles changed from 0 to 90o with step of 1o. To prepare DNA samples, Na-DNA produced by SERVO was moisten by small amount of water to ensure humidity which corresponds to approximately 15 water molecules per one base of DNA (100% humidity) at room temperature [6]. Then DNA fibers were mechanically aligned in a given direction, therefore ensuring the alignment of DNA molecules. The humid sample was spread on the plate transparent in IR region, and then dried at room temperature. The DNA samples were arranged so, that the slit of the spectrometer was parallel to the DNA fibers.G
4-141 and G4-142 generators were used as a sources of the electromagnetic radiation. The power of radiation was less than 10 mW/cm2 , the frequency was tuned in the 37.5-78.5 GHz range. The electromagnetic radiation was applied to DNA during drying of the samples. Experiments were repeated 5 times for each frequency of radiation.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The parameters of the spectra of the DNA samples, prepared in the electromagnetic field, were compared with the parameters of the spectra of the reference DNA samples. In the nonpolarized spectra of irradiated DNA, only very slight changes could be registered, but these changes were well pronounced in polarized spectra (fig.1). The drastic changes in polarized spectra were observed in the region of C=O stretching (1500-1700 cm-1) and PO-2 symmetrical and antisymmetrical stretching (1100-1300 cm-1) vibrations and in the range of "fingerprints"(480-650 cm-1). A new structural band has been appeared near 1450-1500 cm-1 region for the DNA sample prepared in the electromagnetic field. In the 1500-1700 cm-1 region, the number of components for irradiated samples is less than for the reference sample, and thre relative intensities of the bands are redistributed (fig.1).
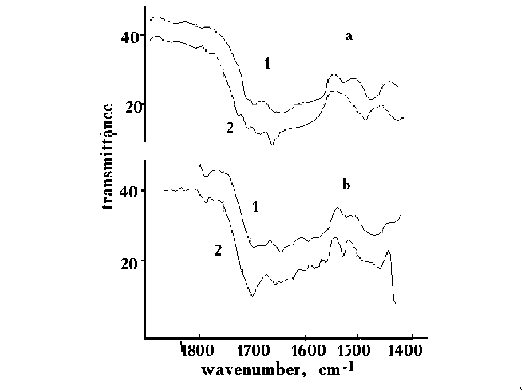
Fig.1. IR polarized spectra of DNA with 76% humidity on KRS-5 substrate, prepared in the weak electromagnetic field with 60.0 GHz frequency (1), and of the reference DNA (2) for 900 (a) and 00 (b) polarization angels.
The changes in spectral parameters of the bands for the irradiated DNA as compared with those for the reference DNA are greater for the angle of polarization of 00 (fig.1 a, b ) than of 90o . From the comparison of the polarized spectra of irradiated DNA for different angles of polarization (0,1, 3, 5,7, 10, 15, 900 ) and for different spectral regions with the same parameters for the reference DNA one can conclude, that the values and directions of dipoles of the C=O bonds (fig.2) in the DNA bases have been changed. Changes in the direction of the dipole moments is equal to or less than 10 .
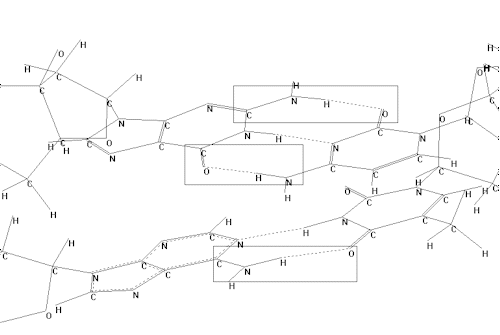
Fig.2. Fragment of structure of DNA molecule; the molecular groups which are supposed to
undergo changes are marked by rectangle boxes.
CONCLUSION
1.The changes were observed in the spectral parameters of the polarized spectra for the DNA prepared in the weak electromagnetic field as compared to those for the reference Na-DNA. These changes are not connected with DNA B-form transition into A-form and consequent disordering. The changes in the rate of loosing water and in spectral parameters are opposite to those expected for B-A transition [7] .
2.The values and directions of transition moments of the C=O bonds of DNA bases have been changed. This can be caused by changes in the third order space structure of DNA molecule as a whole (fig.2).
REFERENCES
G.I.Dovbeshko, G.S.Litvinov, "Mm-wave radiation effect on the spectral characteristics of infrared absorption bands of free and intracellular DNA", Trans. of 1st Congress Europ. Bioelectromagnetic Association, Brussels, Belgium, p.47, 1992.
D.N.Govorun, V.D.Danchuk,, Ya.R. Mishchuk, I.V.Kondratyuk, M.F.Radomsky, M.V.Zheltovsky, " Mirror symmetrical conformational states of canonical nucleic acid bases", Reports of Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, N2, pp.66-69, 1992 (Rus.).
S.S.Urazovsky, Molecular polymorphism, Kiev, AN Ukr.SSR, 336 p. 1956 (Rus.).
S.G.Stepanyan, High resolved vibrational spectra and structure of nucleic acid bases, FTINT AN UkrSSR, 1988, 16P.
P.
F.S.Parker, Application of Infrared, Raman, and Resonance Raman Spectroscopy in Biochemistry, Plenum Press, New York, ch.9, 1983.T.Bolbuch, M.A.Semenov, V.A.Maleev, V.V.Sechkin, ‘Use of the method of piezomicrobalance for obtaining of polynucleotides hydration isotherms", Preprint N 228, Kharkov, IRE Ukr.SSR, 18 p.,1983 (Rus).
E.A.Andreev,T.V.Bolbuch, G.M.Glibitsky, V.N.Kharkyanen, " Influence of millimeter electromagnetic radiation upon the interaction with water and Na-DNA, VII Conf. Spectrosc. Biopolymers, Kharkov, 1-4 Oct., pp.6-7, 1991 (Rus.).