Do furocoumarins induce different kinds of DNA-protein cross-links?
F.Bordin, C.Marzano, F.Carlassare, M.Simonato, A.Guiotto and F.Baccichetti
Dep. Pharmaceutical Sciences of Padova University; Centro di Studio sulla Chimica del Farmaco e dei Prodotti Biologicamente Attivi del C.N.R. (associated to the National Institute for the Chemistry of Biological Systems) - C.N.R.; Padova, Italy.
INTRODUCTION
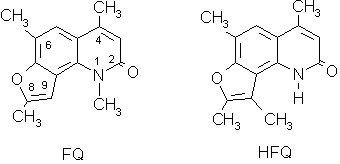 |
We have recently studied some properties of two angular furoquinolinones, which can be regarded as angelicin isosters, 1,4,6,8-tetramethyl-2H-furo[2,3-h]quinolin-2-one (FQ) and 4,6,8,9-tetramethyl-2H-furo[2,3-h]-quinolin-2-one (HFQ).
The main difference in the structure is at N1, which carries a methyl group in FQ and a hydrogen atom in HFQ. Both compounds are characterised by a strong capacity of damaging DNA and a high photosensitizing activity. Table 1 shows the damage induced in DNA in comparison with 8-MOP.
Table 1 - Activity relative to 8-MOP |
||||
Compound |
SSB |
ISC |
DNA binding |
DPC |
HFQ |
0.18 |
0.01 |
5.70 |
2.40 |
FQ |
0.20 |
0.01 |
9.56 |
8.50 |
8-MOP |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
SSB: single strand breaks; ISC: inter-strand cross-links; DPC: DNA-protein cross-links.
As shown, FQ and HFQ are completely unable of inducing inter-strand cross-links (ISC) [1], but form a lot of C4-cycloadducts in DNA [2]. They induce another severe kind of lesion, that is a number of DNA-protein-cross-links (DPC) [1]. In this paper we are showing some data obtained studying the relationship between the formation of DPC and the biological activity of such compounds.